A Tunable Magnet-Based Tactile Sensor Framework
Published in 2020 IEEE SENSORS, 2020
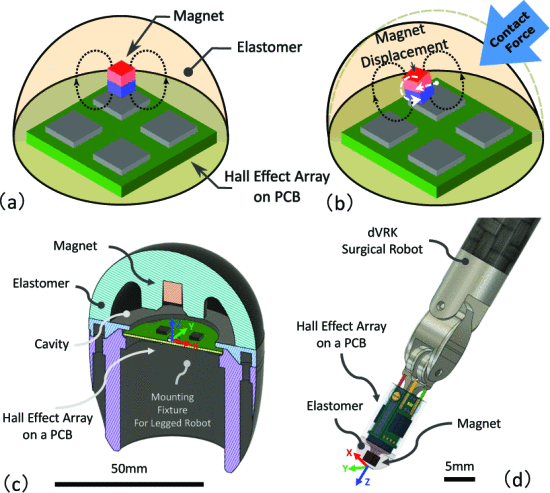
This paper presents an innovative tactile sensor framework based on magnetic field sensing principles, offering tunable sensitivity and robust performance for advanced robotic and biomedical applications. The work addresses key limitations in traditional tactile sensing by leveraging the unique properties of magnetic field interactions.
Technical Innovation: The magnet-based approach offers several advantages over conventional tactile sensing methods:
- Non-contact Sensing: Magnetic field detection enables sensing without direct electrical contact
- Tunable Sensitivity: Adjustable sensor parameters allow optimization for different applications
- Robust Performance: Magnetic sensing is less susceptible to environmental interference compared to resistive or capacitive methods
- Multi-modal Capabilities: Potential for detecting multiple force components and contact geometries
Framework Architecture: The sensor framework integrates:
- Magnetic Field Sources: Strategically positioned magnets to create measurable field patterns
- Magnetic Sensors: High-resolution magnetometers or Hall effect sensors for field detection
- Signal Processing: Advanced algorithms to interpret magnetic field changes as tactile information
- Calibration Systems: Methods for tuning sensor sensitivity and response characteristics
Applications and Advantages: The tunable nature of the sensor framework makes it suitable for diverse applications:
- Medical Robotics: Precise force feedback for surgical and diagnostic procedures
- Prosthetic Devices: Tactile sensation for amputee patients with adjustable sensitivity
- Industrial Automation: Robust sensing in harsh environments where traditional sensors fail
- Research Platforms: Configurable sensing for experimental robotics applications
Sensing Principles: The magnetic-based approach works by:
- Detecting changes in magnetic field strength and direction as objects interact with the sensor
- Converting magnetic field variations into tactile information about contact force, location, and material properties
- Providing continuous, real-time feedback without mechanical wear or electrical degradation
Research Significance: This work represents a significant advancement in tactile sensing technology by:
- Addressing Durability: Magnetic sensors have fewer moving parts and less wear compared to mechanical alternatives
- Enabling Tunability: Allowing sensor characteristics to be adjusted for specific applications
- Improving Reliability: Reducing susceptibility to environmental factors that affect other sensing modalities
- Expanding Applications: Opening new possibilities for tactile sensing in challenging environments
Collaborative Development: The research combines expertise from multiple disciplines at Carnegie Mellon University:
- Robotics Engineering: System integration and control algorithms
- Biomedical Engineering: Bio-inspired design and medical applications
- Sensor Technology: Advanced magnetic sensing and signal processing
- Materials Science: Optimization of magnetic materials and sensor construction
The tunable magnet-based framework represents a versatile platform for tactile sensing that can be adapted to a wide range of applications while providing robust, reliable performance in diverse operating conditions.
Recommended citation: E. Harber, E. Schindewolf, V. Webster-Wood, H. Choset, and L. Li. (2020). "A Tunable Magnet-Based Tactile Sensor Framework." 2020 IEEE SENSORS. pp. 1-4.
Download Paper
